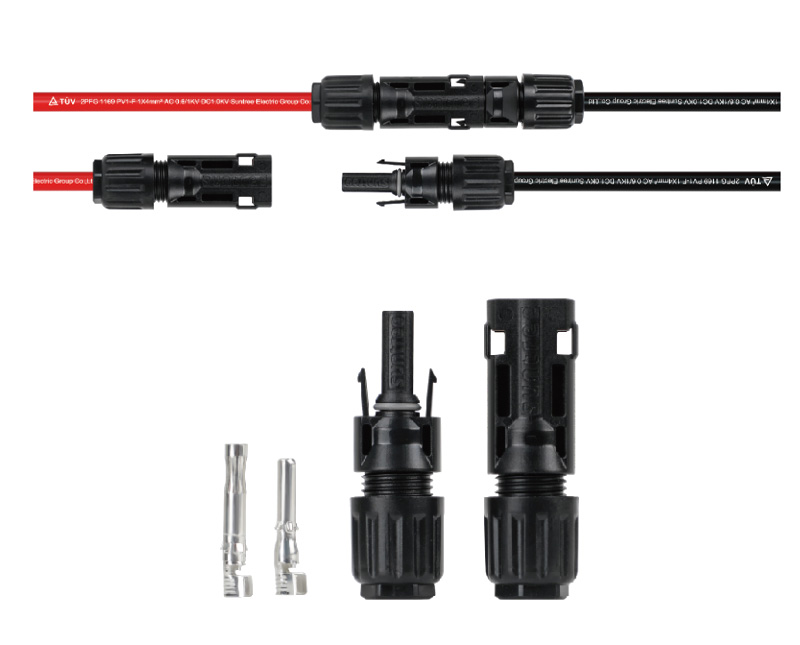
How to use the Solar cable
Cables play a vital role in modern power transmission and the connection of various electrical equipment. Using cables correctly can not only ensure the safe and stable operation of power systems but also extend the service life of cables and improve the efficiency of energy transmission. The following are the basic steps and key points for cable usage:

I. Cable Usage Steps
1. Planning and Selection
Before starting any electrical installation project, first select the appropriate specification of cables according to factors such as the power load to be transmitted, voltage level, and the usage environment. For general household electricity use, such as lighting and small electrical appliances, cables with a lower voltage level and a smaller cross-sectional area may be sufficient. However, for industrial equipment or large-scale power transmission projects, it is necessary to accurately calculate according to the specific power requirements and choose cables that can carry the corresponding current and meet safety standards. For example, a production line in a small factory may need to use cables with a rated voltage of 400V and a cross-sectional area of 16 square millimeters to ensure stable power supply.
2. Installation Preparation
Before installing the cables, carefully check whether the appearance of the cables is damaged and whether the insulation layer is intact. Meanwhile, prepare necessary installation tools, such as cable cutters, wire strippers, crimping pliers, etc., and ensure the safety of the installation site to avoid additional damage to the cables during the installation process.
3. Laying and Connection
Lay the cables according to the design plan. Cables can be laid overhead, underground, or in cable trays. During the laying process, pay attention to avoiding excessive bending, twisting, or stretching of the cables, and ensure that the natural bending radius of the cables meets the specified requirements. For example, for most cables, the bending radius should be no less than 6 times the outer diameter of the cable. When it is necessary to connect the cables, strictly follow the connection process to ensure that the connection is firm and the contact is good. For larger-sized cables, professional cable connectors and crimping tools may be needed to ensure the reliability and conductivity of the connection.
4. Fixing and Identification
After the laying is completed, use cable clips or cable trays and other fixing devices to fix the cables in the appropriate positions to prevent them from moving or shaking. Meanwhile, clearly label the cables with different uses and directions so that the corresponding cable lines can be quickly and accurately found during future maintenance and inspection work.
II. Q&A about Solar Cable
(I) What are the differences between solar cables and ordinary cables?
Solar cables are specially designed for solar power generation systems. Compared with ordinary cables, they have the following notable characteristics:
Insulation Performance: The insulation materials of solar cables usually adopt materials with better weather resistance, such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), which can withstand harsh environmental conditions such as ultraviolet radiation, high temperature, and humidity for a long time. However, the insulation materials of ordinary cables may not be able to maintain good insulation performance under such harsh outdoor conditions for a long time. For example, after several years of outdoor exposure, the insulation layer of ordinary cables may crack and age, resulting in a decline in insulation performance, while the insulation layer of solar cables can maintain relatively stable performance to ensure the safety of power transmission.
Temperature Adaptability: During the operation of solar power generation systems, cables may be affected by relatively high temperatures, especially near solar panels under direct sunlight. Solar cables are specially designed to work normally within a wide temperature range, generally able to withstand temperature changes from -40°C to 125°C. In contrast, the working temperature range of ordinary cables is relatively narrow and may not be able to operate stably under such extreme temperature conditions.
(II) How to choose the appropriate specification of solar cables?
When choosing the appropriate specification of solar cables, the following factors are mainly considered:
Current-Carrying Capacity: Determine the required current-carrying capacity of the cables according to the power and output current of solar panels. You can calculate the maximum output current of solar panels and refer to the cable ampacity table to choose cables with an appropriate cross-sectional area. For example, if the maximum output current of solar panels is 20A, according to the ampacity table, it may be necessary to choose solar cables with a cross-sectional area of 4 square millimeters to ensure that the cables will not overheat due to overload during normal operation, which would affect the cable life and system performance.
Voltage Level: The voltage level of the solar power generation system is also an important basis for choosing cables. Common voltage levels of solar systems include 12V, 24V, 48V, and higher medium-voltage systems. Ensure that the rated voltage of the selected cables can meet the voltage requirements of the system and has a certain margin to cope with possible voltage fluctuations.
Environmental Factors: Consider the installation environment of the cables, such as whether they are exposed to sunlight, whether they need to be laid underground, and whether there are chemical corrosive substances around. If the cables will be exposed outdoors under sunlight for a long time, solar cables with good weather resistance should be preferentially selected. If they are in an environment with a risk of chemical corrosion, such as near the seaside or chemical plants, cables with anti-corrosion outer layer materials should be chosen.
(III) What are the precautions for the installation of solar cables?
The following points should be noted when installing solar cables:
Avoid Mechanical Damage: During the installation process, pay special attention to preventing the cables from being damaged mechanically, such as being scratched by sharp objects or being squeezed by heavy objects. Because even slight damage may damage the insulation layer of the cables, leading to safety hazards such as electric leakage or short circuit. For example, when cables pass through walls or cable trays, ensure that the edges of the holes are smooth and use appropriate protective sleeves to protect the cables.
Correct Wiring Method: The wiring of solar cables should avoid crossing with other power lines or signal lines as much as possible to prevent electromagnetic interference. Meanwhile, wire the cables according to the specified bending radius to avoid excessive bending that may damage the internal structure of the cables. Generally speaking, the minimum bending radius of solar cables should be no less than 6 - 8 times the outer diameter of the cables. The specific value can be referred to the product manual of the cables.
Reliable Connection: The connection parts of the cables are relatively weak links in the whole system. Therefore, ensure the reliability of the connection. When connecting solar cables, use dedicated cable connectors and strictly follow the connection process, such as correct wire stripping and crimping, to ensure that the contact resistance at the joints is small enough to reduce heat generation and energy loss. After the connection is completed, necessary insulation tests and electrical performance tests should be carried out to ensure that the connection quality meets the requirements.
In conclusion, whether it is ordinary cables or solar cables, the correct usage and installation methods are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of power systems. In actual operation, it is necessary to follow relevant electrical installation specifications and the technical requirements of cable products to ensure that the cables can perform at their best and provide reliable power transmission for various electrical equipment.